A |
adjacent angles: a pair of angles which share a common side
altitude: the line segment which extends from the top of an figure/object
to its bottom in such a way that the length of this segment corresponds to the "height"
of the entity; in the context...
...of a
triangle, extends from
one of the vertices to a point on the line which contains the side (a.k.a., base) opposite
of that angle such that it forms a
perpendicular intersection with the line
...of a
trapezoid, extends from one
of the parallel sides to the line segment containing the other (opposite) side such that it
forms a perpendicular intersection with
the parallel side; both the parallelogram
and rhombus figures are applicable entities
analogous: similar or equivalent in some respect(s) but otherwise different;
corresponding in some aspect(s); similar in function but not in structure or origin
a priori: (Latin) literally, "before the fact;" pertaining to or
characterized by something which does not depend on observation or prior experience
arbitrarily: randomly or without a specific bias, cause or reason
arithmetic mean: a type of average (measure of central tendency),
which is defined as the sum of all the values in a set of numerical data divided
by n (where n = # of values in the data set); this
value is usually the most common usage of the word "average," and typically it
is labeled as either µ (lowercase
Greek letter "mu")
to denote a population mean or
x (referred to a "x bar")
to denote a sample mean
|
B |
Bell curve: a.k.a. the normal curve, is an idealized statistical
graph of a frequency (or relative frequency) distribution for a random variable quantity
whose mean,
median and
mode are identical; the distribution
is symmetrical about this (center-line) value.
bimodal: pertaining to a set of data values in which there are two modes
(trimodal refers to three modes, etc.); see
mode
|
C |
circle: two-dimensional, closed curve consisting of all points which
are equidistant from a center point
Circumference: the distance around a circle, often denoted by the
(uppercase letter) C; it is found by either of the quantities 2πr
(where r is the length of the
radius) or πd
(where d is the length of the
diameter)
coefficient: a quantity (usually a numerical constant) which is multiplied
by another quantity following it in an expression; e.g., in the algebraic expression
4x2
- 6 x,
the coefficient of (the first term) x2
is 4 and the coefficient of (the second term) x is -6.
complementary angles: two (adjacent) angles which form a right angle;
i.e., the sum of their angle measures is 90°
composite figure: any 2-dimensional figure whose composition consists of
simpler figures (e.g., triangles, squares, rectangles, circles, etc.) or portions thereof
composite object: any 3-dimensional object whose composition consists of
simpler objects (e.g., cubes, polygonal prisms, spheres, cones, etc.) or portions thereof
congruent figures: any two-dimensional figures (usually with reference to
polygons), which are identical in
shape and size (contrast with similar figures)
congruent objects: any three-dimensional objects (usually with reference to
polyhedra), which are identical in
shape and size (contrast with similar objects)
cube root: the cube root of any quantity x, denoted as
either3Ö xor
x1/3,
is defined as the value of y where y 3 = x
|
D |
diagonal: line segment extending from one of the
vertices of a
polygon to a non-adjacent,
vertex
diameter: a line segment whose two endpoints lie on a
circle and which pass through the
center of the circle
|
E |
equilateral: all sides being of equal length, usually in reference to a
triangle whose three sides are all the
same (length) and whose three interior angles are all congruent (each one measuring 60°)
Erathosthenes: the Greek-born scholar and director of the Library of Alexandria
(ca. 300 B.C.E.) who is historically credited with
deducing an estimate for the
Circumference of the Earth
extrapolate: to find an estimate of a value beyond a set of given values
(in a sequence), based on the prevailing pattern or tendency (often a proportion) of the
original values
|
F |
factor: [n] any of the quantities involved in a multiplication; [v] to express
a given quantity as a product of two or more (typically simpler or prime) quantities
frequency: the number of times an element of data occurs (in the raw data),
or the collective number of data elements that occur in a specific category (of the group data)
frequency distribution: a statistical inventory (usually in table format)
which indicates the frequency with which each data element occurs (in the raw data) or
the collective frequency of data elements occuring in a specific category (of the group
data); its associated graph, e.g. a
histogram, is also commonly
referred to as the frequency distribution (although it is implicitly understood to be only the
graphical representation of the distribution rather than the literal "frequency distribution"
itself) — see section 4.1 practice
problem (America's Nat'l Parks)
|
G |
geometric mean: a type of average (measure of central tendency), which
is defined as the "n-th" root of the product of all the values
in a set of numerical data (where n = # of values in the data set)
Greek Alphabet: 24-character alphabet which is used to write the Greek
language; it is often considered the oldest extant alphabet, having been used since circa the
8th or 9th century B.C.E. (click here to view the alphabet
w/pronunciation key)
|
H |
harmonic mean: a type of average (measure of central tendency)
which is defined as the quotient of n divided by the sum of the
reciprocals of all the values in a set of numerical data (where n
= # of values in the data set)
hectare (ha): a Metric System unit of land area
defined as 1 square hectometer (and which is equivalent to 10,000 square meters)
hectometer (hm): a Metric System
unit of length defined as 100 meters
Heron's Formula: formula for finding the Area of a
triangle when the lengths of all
three sides (a, b, and c) are known. It involves a
(square root) computation using the semiperimeter, which is defined as one-half
of the Perimeter
(i.e., s = ½P where P = a + b + c)...
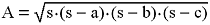 hexagon: a six-sided polygon
histogram a bar-chart or graph depicting with (vertically-directed) rectangles the
frequency distribution of the elements in a set
of data; the height of each rectangle represents the known
frequency for the given data element (in the
raw data) or the collective frequency of data
elements occuring in a specific category (of the group data)
hypotenuse:
the side opposite of the right angle in a
right triangle, it is always the
longest of the three sides; in standard
triangle notation (where the sides
are labeled a, b and c) it is generally the side of length c
hexagon: a six-sided polygon
histogram a bar-chart or graph depicting with (vertically-directed) rectangles the
frequency distribution of the elements in a set
of data; the height of each rectangle represents the known
frequency for the given data element (in the
raw data) or the collective frequency of data
elements occuring in a specific category (of the group data)
hypotenuse:
the side opposite of the right angle in a
right triangle, it is always the
longest of the three sides; in standard
triangle notation (where the sides
are labeled a, b and c) it is generally the side of length c
|
I |
Infinity: (∞) quantity whose value is unbounded
Integers: set of numbers which include all of the
Whole
numbers combined with the set of negative values of the
Natural
numbers; frequently represented as
I = {...,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,...}
interpolate: to find an intermediate value between two known values
(in a set of values), based on a specific pattern, e.g., a proportional amount (used
in linear interpolation), of the original values... [Linear Interpolation Calculator]
irrational numbers: subset of real numbers whose decimal representations
neither repeat nor terminate; may also be defined as the subset of real numbers which are not
rational numbers (e.g., both
Ö2
and π are irrational)
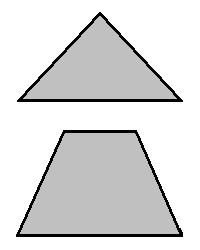 isosceles: having a pair of base angles which are congruent,
usually in reference to a triangle
but also sometimes with reference to a
trapezoid (as respectively depicted
in the illustration, shown at right); moreover, the two corresponding sides are equal in length
isosceles: having a pair of base angles which are congruent,
usually in reference to a triangle
but also sometimes with reference to a
trapezoid (as respectively depicted
in the illustration, shown at right); moreover, the two corresponding sides are equal in length
|
J |
judicious: characterized by good sense or judgment;
proceeding from keen insight and pragmatic priority for a desirable result
|
K |
|
L |
laissez-faire: (french) philosophical policy of tolerance
toward and non-interference with other's affairs
|
M |
mean: a type of average (measure of central tendency); see either
arithmetic mean,
geometric mean,
harmonic mean, or
quadratic mean
median: middle number in a set of numerical data when when it is
arranged in (either ascending or descending) order; for data sets with an even number
of data values then the middle value is a hypothetical value which lies halfway between
the two middle values
mind mapping: an alternative method of notetaking, one which uses an
artistic (stream of consciousness) approach...
mode: the most frequent number(s), which must occur more than once;
there may not be a mode or there may be more than one (see
bimodal)
modeling: (mathematical) describing a physical phenomenon
by logical principles characterized with quantitative relationships, e.g.,
formulas, whose parameters may be measured (or experimentally determined)...
|
N |
Natural numbers: set of counting numbers; frequently represented as
N = {1,2,3,...}
nomenclature: a set or system of names or terms, as those used in a
specific science, art, industry, etc.
non-sequitur: a conclusion which does not (logically) follow from its
supporting arguments (premises)
normal distribution:
a statistical distribution of data values in which the (arithmetic) mean,
median, and mode
are each equal; the graph is a
bell-shaped curve
symmetric about the vertical line through its peak and wherein the percentage of data values within one
standard deviation of the
mean is about 68.26%, the percentage of data values within two
standard deviations of the
mean is about 95.44%, and about 99.75% of the data values are within three
standard deviations of the mean...
|
O |
oblique: characterized by an angle which is not a right angle
obtuse: characterized by an angle whose measure is between 90° and 180°
(non-inclusive of these two limiting values themselves)
octagon: an eight-sided
polygon
|
P |
parallelogram: a
quadrilateral whose (two) pairs of
opposing sides are both parallel and whose (two) pairs of opposing interior angles are
congruent; although a rectangle is a special case of the parallelogram, it usually refers to a
quadrilateral whose interior angles
are not right (90°) angles
pentagon: a five-sided
polygon
perimeter: the distance around a
polygon, often
denoted by (the uppercase letter) P
perpendicular: characterized by an angle of intersection which is a
right angle, typically in reference to a two-dimensional figure; in higher dimensions
this property is usually referred to as "orthogonality" (being orthogonal)
pi: the (irrational,
transcendental) number defined as the
circumference of a
circle divided by its
diameter, conventionally denoted by
the (lowercase Greek letter)
π. It is approximately equal to
3.14159265358979323846264338327950288419716939937510
and has been calculated to over 200 billion decimal places!
More
about π?
polygon: a closed, two-dimensional figure of three or more sides, each of
which are (straight) line segments; see
triangle,
quadrilateral,
pentagon,
hexagon, etc.
polyhedron: a three-dimensional solid whose exterior consists solely of polygons
(i.e., flat faces and straight edges); the plural form is "polyhedra"
prism: a three-dimensional object (solid) with at least two parallel faces AND with consistent
cross-sectional Areas (i.e., the two-dimensional sections are ALL congruent)
Pythagorean Theorem:
a historically renowned formula relating the three sides of a
right triangle. If a
and b represent the lengths of the two shorter sides (a.k.a. legs) and
c represents the length of the longest side (a.k.a. the
hypotenuse), then --
a2 + b2 = c2
|
Q |
QED: (latin) literally, "quod erat demonstrandum" — meaning that which was
to be demonstrated, used to formally earmark the end of a logical or mathematical proof
quadratic mean: a type of average (measure of central tendency), which
is defined as the square root of the quotient of the sum of the squares of all the
values in a set of numerical data divided by n (where n
= # of values in the data set)
quadrilateral: a four-sided polygon; examples include squares, rectangles,
parallelograms,
trapezoids, etc.
|
R |
radian: a unit of angle measure defined as the measure of an angle whose
intercepted arc is equal to the radius of the circle when the angle's vertex is positioned
at the center of the circle. Consequently, 2π radians = 360° and thus
one radian is 180/π degrees or approx. 57.3°. The unit of
radians is most typically used in trigonometry and frequently the unit is omitted such
that the value of the angle's measure is, by convention, merely understood to be radians
(i.e., in the absence of any other indicated unit such as degrees, minutes, and/or
seconds)...
radius: a line segment which extends from the center of a
circle to any point of the
circle itself
rational numbers: set of numbers formed by the ratio (i.e., fraction) of two
Integers where zero in the denominator
is not permitted (division by zero is undefined); frequently represented as
Q = {a/b | a Î I, b Î I, b ≠ 0}
regular polygon: an equilateral
polygon; i.e., one whose
sides are each identical in length AND whose interior angles all have the same measure
relative (percentage) error: ratio of the absolute error to the actual (or
true) value, where the absolute error is the difference between the estimate (or measured
value) and the actual (or true); this ratio is then typically expressed as a percent...
| err% = | estimate - actual value |
|---|
|
|---|
| actual value |
|---|
right triangle: a
triangle which contains a "right"
angle (whose measure is 90°); in the conventional "a, b, c" labeling of the three
sides, the side of length "c" will represent the
hypotenuse
|
S |
scalene: having all sides unequal, usually in reference to a
triangle
SI: Systeme International (french) = International System
similar figures: any two-dimensional figures (usually in reference to polygons)
which are identical in shape but different in size (contrast with congruent figures)
similar objects: any three-dimensional objects (usually in reference to polyhedra)
which are identical in shape but different in size (contrast with congruent objects)
square root: the square root of any quantity x, denoted as either
Ö xor
x1/2,
is defined as the value of y where y 2 = x
standard deviation: numerical measure of the variation or dispersion in
a set of numerical data, which is defined as square root of the quotient of the sum
of the squares of all the deviations from the
arithmetic mean
divided by n for a
population or by n
- 1 for a sample (where
n = # of values in the data set); the (lower-case
Greek letter, "sigma") σ
is typically used to denote the value for a
population while "s" denotes
the value for a sample
straight angle: an angle whose initial and terminal sides form a
straight line, its measure being 180° (or π radians)
subtend: to extend under or to be opposite of
supplementary angles: two (adjacent) angles which form a straight
angle; i.e., the sum of their angle measures is 180°
surmise: infer from incomplete evidence or knowledge; imagine to be the case, true or probable
symmetric: similar in size, shape and the relative position of corresponding parts; proportioned
in a manner such that half of the figure/object is the "mirror-image" of the other half, e.g.,
a circle is symmetric about its diameter, a rectangle is symmetric about a diagonal, etc.
|
T |
tangent: (1) a line which touches or intersects a curve at one point
in the immediate vicinity of the point (in the case of a circle, it touches the
curve only once); (2) a trigonometric ratio defined, in terms of a
right triangle, as the length of
the opposite side divided by the length of the adjacent side
(w.r.t. a specified angle)
transcendental numbers: subset of real numbers whose value cannot be expressed as the solution
to a polynomial equation -- hence they cannot be a square root,
cube root, etc. (even though they are
irrational numbers); examples of transcendental numbers
include both "π" and "e"
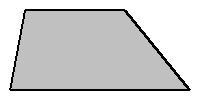 trapezoid: a quadrilateral
possessing, at least, two parallel sides (as depicted in the illustration, shown at right)
triangle: a three-sided polygon
trapezoid: a quadrilateral
possessing, at least, two parallel sides (as depicted in the illustration, shown at right)
triangle: a three-sided polygon
|
U |
unit price: cost per unit for a specific good
or service (e.g., the price of gasoline might be
$2.25 per gallon)
— see section 1.2
|
V |
vertex: shared endpoint of two rays (or line segments) which form an angle;
"vertices" is the plural of "vertex"
vertical angles: pair of opposing angles whose (common or shared)
vertex is the intersection point of two straight lines; the measures of any pair of vertical
angles are always equal
|
W |
Whole numbers: set of numbers which include zero
(0) and all of the
Natural
Numbers; frequently represented as W = {0,1,2,3,...}
|
X |
|
Y |
|
Z |
z-score: the value assigned or computed to a raw data (x)
value by subtracting the
arithmetic mean (µ) from it and then
dividing the difference by the
standard deviation
(σ); i.e.,
zi = (xi - µ) / σ
|



